The Nervous SystemIntroduction:
Central Division:
Peripheral Division:
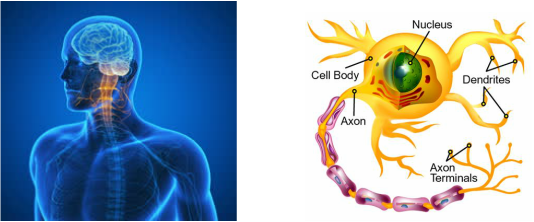
Neurons, Brain, & Spinal Cord:
The spinal cord is considered to be an "information highway", which connects the peripheral nervous system to the brain. It is protected by 31 vertebrae. At each segment of bone a pair of spinal nerves branch out. The spinal cord receives information from sensory and motor neurons. Sensory receptors send information along sensory neurons to the spinal cord. From here it is passed via interneurons to motor neurons that lead to muscles in the body. This causes movement. Sensory neurons can also send information through the spinal cord into the brain stem, to then be processed by the thalamus, the sensory switchboard of the brain (except for smell). Spinal cord disorders can be caused by injuries, infections, a blocked blood supply, or compression by a fractured bone or tumor. The muscles can be become weak or paralyzed and sensation can be abnormal or lost. Often, in order to recover as much function as possible, rehabilitation is needed.
Diseases of the Nervous System:Nerve Disorders
General Information About Nervous System DisordersNervous system disorders can come from abnormalities with one's nervous system, this can be brought on by: trauma, infections, degeneration, structural defects, tumors, blood flow disruption, and auto immune disorders. These disorders usually have some of these symptoms: odd persistent headaches, loss of feeling/tingling, weakness, loss of vision, memory loss, impaired mental ability, lack of coordination, muscle rigidity, tremors & seizures, pain, muscle wasting, and slurred speech. There are also two kind of nervous system disorders when concerning the brain. Abnormalities that come from odd development of the brain prior to birth is a neurological disorder since it concerns how you are neurologically set up, this includes disorders such as schizophrenia and the autism spectrum. Disorders that are gained from some form of damage during life are mental disorders. This includes things such as depression.
Parkinson's Disease: A nervous system disease that causes gradual deterioration of ones motor skills (less facial expressions, slower walking, less arm movement, slurred speech, etc.) This disease usually starts with slight tremors in the hand. The effects are gradual and worsen as they go on. Bell's Palsy: This causes intense amounts of facial paralysis to part of your face. The disease does not have a known cause, however there is medication to take for it and it is possible to recover from. Cerebral Palsy: This disorder that comes from experiencing physical head trauma around and during the time of ones birth. Possible symptoms might include, limited motor skills, limited mental capabilities, abnormalities from limb contractions, epilepsy, visual impairment, squint, reduced hearing, and behavioral problems. Motor Neuron Disease: Deterioration of someones motor system during middle age. It is a disease that is inherited and may affects one's spinal cord and nuclei in the brain and causes muscle weakness. Epilepsy Seizures: General seizures: all areas of the brain are involved. Multiple Sclerosis: Affects are commonly seen in young and middle aged adults. The disorder is brought about through damage to the coating around nerve cells, this impairs the function of the nerve. Symptoms one might experience from this are shaking limbs, involuntary eye movement, problems with pronunciation, and weakness. Sciatica: Common condition is caused by the damaging or compressing of one's nerves or nerve roots. this form of injury can also happen very suddenly. Symptoms might include general pain felt in the back and the legs, stiffness in the back, and/or numbness and weakness in legs. Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RlUPCNLSJIY
References:Balingit, Angelica. “Liver: Anatomy, Definition, Symptoms, and More.” Healthline, 30 May 2018, http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/liver. Accessed 9 June 2022.
Hoffman, Matthew. “The Esophagus (Human Anatomy): Picture, Function, Conditions, and More.” WebMD, 10 July 2020, https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/picture-of-the-esophagus. Accessed 19 November 2022. Hoffman, Matthew. “Liver (Anatomy): Picture, Function, Conditions, Tests, Treatments.” WebMD, 23 June 2021, http://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/picture-of-the-liver. Accessed 19 November 2022. Wedro, Benjamin. “Liver Anatomy & Function Tests, Disease Symptoms & Causes.” MedicineNet, http://www.medicinenet.com/liver_anatomy_and_function/article.htm. Accessed 28 November 2021. |
Paola Arias
|