Cardiovascular or Circulatory System
 https://www.istockphoto.com/photos/cardiovascular-system
https://www.istockphoto.com/photos/cardiovascular-system
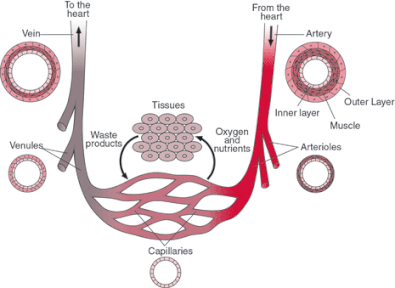
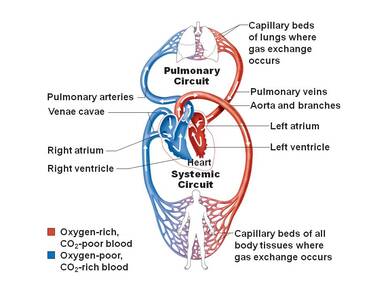
The cardiovascular system consists of three main functions: transportation, protection, and regulation with three main parts; blood, blood Vessels, and the heart. It helps to transport nutrients, gases and waste products to all body tissues, through blood vessels. Veins act as highways to deliver blood to the heart. The blood delivers both nutrients and oxygen while removing waste and carbon dioxide. The cardiovascular system consists of two circulatory loops, the pulmonary loop, and the circulatory loop. The pulmonary loop transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs, from the left side of the heart, to pick up oxygen. While the circulatory loop takes the oxygen rich blood, from the right side of the heat, to all the parts of the body. The circulatory loops are made of blood vessels, which are the body's highway that transport blood, three major types of vessel are arteries, capillaries and veins. The white blood cells act as protectors in our body help get rid of waste that enters our body. Blood carries antibodies in order to build immunity too pathogens that find a way into our system and fight diseases foreign to our bodies.
Nutrient Support FoR the Cardiovascular System
Phytoestrogens: Plants that have a weak estrogen-like action in the body.
|
Are substances in plants such as flaxseed, that have a weak estrogen-like action in the body. Studies suggest that flaxseed lowers the risk of blood clots, stroke, and cardiac arrhythmia. It may also help lower total and LDL "bad" cholesterol and triglycerides, and even blood pressure.
|
Phytosterols: Are plant sterols that chemically resemble cholesterol and may to reduce blood cholesterol. All nuts and seeds, including wheat germ, have phytosterols.
|
High Sterol Whole Foods
|
Carotenoids: Are heart-protective antioxidants in many colorful fruits and veggies. Alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, lutein, and lycopene are carotenoids.
|
High Carotenoid Whole Foods
|
Polyphenols: Are another set of antioxidants that protect blood vessels, lower blood pressure, reduce LDL "bad" cholesterol
|
High Polyphenol Whole Foods
Berries
Vegetables - We need 2.5 to 3 cups of vegetables per day and most contain polyphenols
Coffee and Tea - 35mg/ 1 cup |
Omega-3 fatty acids and Alpha-linolenic fatty acids: Are found in plant foods like walnuts and found in fatty fish like salmon, help boost the immune system, reduce blood clots, and protect against heart attacks. They also increase good HDL levels, lower triglyceride levels, protect arteries from plaque buildup, are anti-inflammatories, and lower blood pressure.
B-complex vitamins: Protect against blood clots and atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries.
Vitamins C and E: Are antioxidants that protect cells from free radical damage.
Top Foods that Increase Circulation & Support the Heart
Almonds & Walnuts: Are high in fiber, vitamin E, and omega 3 fatty acids.
Watermelon: Contains antioxidants called lycopene which improve circulation
Cayenne Pepper: Increases metabolic rate and circulation, it strengths arteries and blood vessels.
Dark Chocolate: Cocoa contains flavonoids which improve blood circulation.
Oranges and other Citrus: Contain vitamin C which prevent poor circulation, reduces artery inflammation and lowers blood pressure.
Ginger: Increases blood circulation.
Salmon and Avocado: Both contain heart-health omega 3 fatty acids which support the cardiovascular system in general.
Oatmeal: Helps reduces cholesterol
Blueberries: Rich in antioxidants.
Green Tea: Reduces blood clots.
Watermelon: Contains antioxidants called lycopene which improve circulation
Cayenne Pepper: Increases metabolic rate and circulation, it strengths arteries and blood vessels.
Dark Chocolate: Cocoa contains flavonoids which improve blood circulation.
Oranges and other Citrus: Contain vitamin C which prevent poor circulation, reduces artery inflammation and lowers blood pressure.
Ginger: Increases blood circulation.
Salmon and Avocado: Both contain heart-health omega 3 fatty acids which support the cardiovascular system in general.
Oatmeal: Helps reduces cholesterol
Blueberries: Rich in antioxidants.
Green Tea: Reduces blood clots.
Basics of the Cardiovascular System
Blood
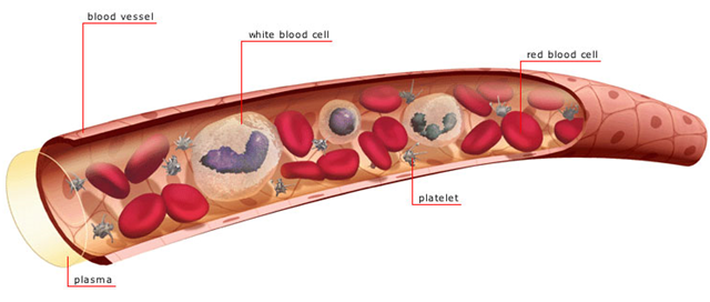
.Blood is what transports nutrients and oxygen to all the parts of the body, it consists of red blood cells, white blood cells, Platelets, and liquid plasma. Red blood cells are what transport oxygen throughout the body, their unique shape increases their surface to volume ratio, and is attributed to the fact that when they are infants they reject their nucleus. White blood cells are small part of the blood in your body, but they are a key part of the immune system, their main function is to eradicate foreign invaders. Plasma is the non-cellular, liquid part of blood. Blood contains three types of cells: white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets.
WHITE BLOOD CELLS: White blood cells are supposed to detect foreign bodies and infection, then kill them by creating antibodies to help the immune system battle off the attack.
RED BLOOD CELLS: Their job is to transport oxygen through your body. Blood goes into your body through the alveoli of the lungs and sticks to the protein hemoglobin.
PLATELETS: They are responsible for clotting your blood when you hurt yourself by sticking to the edges of a cut. If the body has a low level of platelets then clotting may not occur and bleeding can continue. But if the body has too many platelet cells, then clotting can be produced within blood vessels, possibly causing a heart attack or stroke.
WHITE BLOOD CELLS: White blood cells are supposed to detect foreign bodies and infection, then kill them by creating antibodies to help the immune system battle off the attack.
RED BLOOD CELLS: Their job is to transport oxygen through your body. Blood goes into your body through the alveoli of the lungs and sticks to the protein hemoglobin.
PLATELETS: They are responsible for clotting your blood when you hurt yourself by sticking to the edges of a cut. If the body has a low level of platelets then clotting may not occur and bleeding can continue. But if the body has too many platelet cells, then clotting can be produced within blood vessels, possibly causing a heart attack or stroke.
Blood Vessels
|
The blood vessels are what transport the blood throughout the body.
It consists of:
|
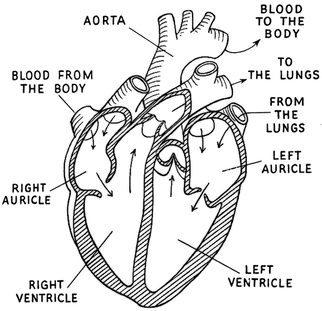
The Heart
|
Heart
The cardiovascular system is centered around the heart, which is capable of pumping 5 liters of blood throughout the body every minute when at rest. The heart is a four chamber "double pump", left side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen, while the right side pumps the oxygen rich blood to all the parts of the body. Consists of 4 chambers: 2 upper chambers (the atria) 2 lower chambers (the ventricles)
Pulmonary Circuit: deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle of the heart through the pulmonary artery and travels to the lungs, then returns as oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart through the pulmonary vein. Systemic Circuit: oxygenated blood leaves the body through the left ventricle to the aorta, and from there enters the arteries and capillaries where it supplies the body's tissues with oxygen. Deoxygenated blood returns through veins to the venae cavae, re-entering the heart's right atrium. |
POOR CIRCULATION
|
Poor circulation is the most common problem of the circulatory system, it occurs when the blood flow to a specific part of the body is reduced. It is most likely to happen in your extremities, such as legs arms. hands and feet. |
SYMPTOMS
|
CAUSES OF POOR CIRCULATION
|
Does Exercise Help and How much is enough?
Exercising 30 minutes a day five days a week will improve your heart health and help reduce your risk of heart disease.
Heart and Vascular Diseases
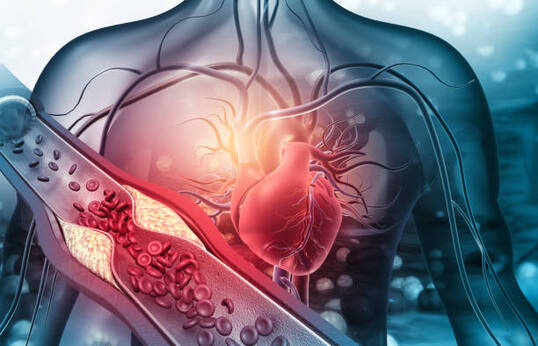
Heart Attack:
Also called "myocardial infarction" , a heart attack happens when blood flow to the heart is severely reduced . Due to the hardening and narrowing of the coronary arteries from the build-up of fat, cholesterol, and other substances, known together as "plaque." A blood clot forms around the plaque, blocking blood flow. This results in permanent damage or death of part of the heart muscle. This is the number one killer in the United States.
Arrhythmia:
It is involve with the the electrical impulses of the heart—not the arteries or blockages. These electrical impulses may happen too fast, too slow, or irregularly, which causes the heart to beat the same way. When the heart doesn’t beat normally, it can’t pump blood effectively to the lungs, brain, and other organs, causing them to potentially shut down or become damaged.
Heart Failure:
Heart failure doesn't mean that the heart is no longer working. Heart failure is when the heart’s ability to pump is weaker Blood moves through the heart and body at a slower rate, pressure increases in the heart, and the heart can’t supply enough blood and oxygen to the body’s cells, resulting in fatigue and shortness of breath.
Congenital Heart Defects
Different than other types of heart conditions, congenital heart defects are present at birth. These defects are not a disease, but rather an abnormality that occurs while a fetus is developing. Examples include a leaky heart valve or malformations in the walls that separate the heart chambers. Some heart defects may produce symptoms at birth or during childhood, while others aren’t discovered until a person is an adult. Treatment may or may not be needed, depending on the severity of the defect.
Cardiomyopathy:
A progressive disease that causes the heart to become abnormally enlarged, thickened, and/or stiffened, cardiomyopathy (also known as heart muscle disease) limits the heart muscle’s ability to pump blood effectively. This often leads to other heart conditions such as heart failure or arrhythmia.
Also called "myocardial infarction" , a heart attack happens when blood flow to the heart is severely reduced . Due to the hardening and narrowing of the coronary arteries from the build-up of fat, cholesterol, and other substances, known together as "plaque." A blood clot forms around the plaque, blocking blood flow. This results in permanent damage or death of part of the heart muscle. This is the number one killer in the United States.
Arrhythmia:
It is involve with the the electrical impulses of the heart—not the arteries or blockages. These electrical impulses may happen too fast, too slow, or irregularly, which causes the heart to beat the same way. When the heart doesn’t beat normally, it can’t pump blood effectively to the lungs, brain, and other organs, causing them to potentially shut down or become damaged.
Heart Failure:
Heart failure doesn't mean that the heart is no longer working. Heart failure is when the heart’s ability to pump is weaker Blood moves through the heart and body at a slower rate, pressure increases in the heart, and the heart can’t supply enough blood and oxygen to the body’s cells, resulting in fatigue and shortness of breath.
Congenital Heart Defects
Different than other types of heart conditions, congenital heart defects are present at birth. These defects are not a disease, but rather an abnormality that occurs while a fetus is developing. Examples include a leaky heart valve or malformations in the walls that separate the heart chambers. Some heart defects may produce symptoms at birth or during childhood, while others aren’t discovered until a person is an adult. Treatment may or may not be needed, depending on the severity of the defect.
Cardiomyopathy:
A progressive disease that causes the heart to become abnormally enlarged, thickened, and/or stiffened, cardiomyopathy (also known as heart muscle disease) limits the heart muscle’s ability to pump blood effectively. This often leads to other heart conditions such as heart failure or arrhythmia.
References
Richter, Amy. “Foods high in estrogen: Benefits, examples, and side effects.” Medical News Today, 29 January 2021, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/foods-high-in-estrogen#definition.
Lappe, Sydney. “What Are Sterols and Stanols? Food Compounds to Know About.” BistroMD, 20 June 2022, https://www.bistromd.com/cholesterol/10-foods-high-in-plant-sterols.
“Carotenoids, carotenoids benefits and carotenoids foods.” Health Jade, https://healthjade.com/carotenoids/.
“The Power of Polyphenols.” Laboratoires Activa, 7 October 2020, https://www.laboratoiresactiva.com/vn/the-power-of-polyphenols/.
“Chokeberry: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews.” WebMD, https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1558/chokeberry.
Pathak, Neha. “Elderberry: Health Benefits, Risks, Uses, Effectiveness.” WebMD, 21 September 2022, https://www.webmd.com/diet/elderberry-health-benefits.
Mikstas, Christine. “8 Foods High in Polyphenols and Why You Need Them.” WebMD, 23 November 2022, https://www.webmd.com/diet/foods-high-in-polyphenols.
How Does the Blood Circulatory System Work? U.S. National Library of Medicine, 6 Jan. 2012, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0047056/.
"5 Tips to Improve Blood Circulation - Johnston Health." Johnston Health. 15 Mar. 2012, http://johnstonhealth.org/2012/03/5-tips-to-improve-blood-circulation/
"Chronic Pain Causes, Symptoms, Treatment - Circulatory Problems - EMedicineHealth." EMedicineHealth. http://www.emedicinehealth.com/chronic_pain/page7_em.htm.
"Super Foods to Help Improve Blood Circulation." Foods That Help to Improve Your Circulation, http://us.revitive.com/health-information/foods-to-improve-circulation/.
"Symptoms and Causes of Poor Circulation." Healthline, http://www.healthline.com/health/poor-circulation-symptoms-causes.
Toro, Ross. "Diagram of the Human Circulatory System (Infographic)." LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 1 Mar. 2013. http://www.livescience.com/27585-human-body-system-circulation-infographic.html.
Images from:
http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/heart_and_blood_vessel_disorders/biology_of_the_heart_and_blood_vessels/blood_vessels.html
"Blood Vessels." Merck Manual Home Edition. N.p., n.d. http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/heart_and_blood_vessel_disorders/biology_of_the_heart_and_blood_vessels/blood_vessels.html.
"Cardiovascular System." InnerBody. N.p., n.d., http://www.innerbody.com/image/cardov.html.
"The 25 Best Foods For Your Heart." Prevention. N.p., n.d., http://www.prevention.com/health/health-concerns/best-foods-heart-health?s=22.
Lewis, Tanya. "Human Heart: Anatomy, Function & Facts." LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 23 May 2013.http://www.livescience.com/34655-human-heart.html.
*"CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM." INNERBODY, HTTP://WWW.INNERBODY.COM/IMAGE/CARDOV.HTML.
*"NEW RELEASES." 5 WAYS TO PREVENT HEART DISEASE, HTTP://WWW.HEALTH.HARVARD.EDU/HEALTHBEAT/THESE-FIVE-HABITS-CAN-SAVE-YOUR-HEART-HERES-HOW.
*LEWIS, TANYA. "HUMAN HEART: ANATOMY, FUNCTION & FACTS." LIVESCIENCE. TECHMEDIA NETWORK, 23 MAY 2013, HTTP://WWW.LIVESCIENCE.COM/34655-HUMAN-HEART.HTML.
YouTube, 2 July 2022, http://charlottewellnessclinic.blogspot.com/2010/03/different-parts-of-blood.html.
Lappe, Sydney. “What Are Sterols and Stanols? Food Compounds to Know About.” BistroMD, 20 June 2022, https://www.bistromd.com/cholesterol/10-foods-high-in-plant-sterols.
“Carotenoids, carotenoids benefits and carotenoids foods.” Health Jade, https://healthjade.com/carotenoids/.
“The Power of Polyphenols.” Laboratoires Activa, 7 October 2020, https://www.laboratoiresactiva.com/vn/the-power-of-polyphenols/.
“Chokeberry: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews.” WebMD, https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1558/chokeberry.
Pathak, Neha. “Elderberry: Health Benefits, Risks, Uses, Effectiveness.” WebMD, 21 September 2022, https://www.webmd.com/diet/elderberry-health-benefits.
Mikstas, Christine. “8 Foods High in Polyphenols and Why You Need Them.” WebMD, 23 November 2022, https://www.webmd.com/diet/foods-high-in-polyphenols.
How Does the Blood Circulatory System Work? U.S. National Library of Medicine, 6 Jan. 2012, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0047056/.
"5 Tips to Improve Blood Circulation - Johnston Health." Johnston Health. 15 Mar. 2012, http://johnstonhealth.org/2012/03/5-tips-to-improve-blood-circulation/
"Chronic Pain Causes, Symptoms, Treatment - Circulatory Problems - EMedicineHealth." EMedicineHealth. http://www.emedicinehealth.com/chronic_pain/page7_em.htm.
"Super Foods to Help Improve Blood Circulation." Foods That Help to Improve Your Circulation, http://us.revitive.com/health-information/foods-to-improve-circulation/.
"Symptoms and Causes of Poor Circulation." Healthline, http://www.healthline.com/health/poor-circulation-symptoms-causes.
Toro, Ross. "Diagram of the Human Circulatory System (Infographic)." LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 1 Mar. 2013. http://www.livescience.com/27585-human-body-system-circulation-infographic.html.
Images from:
http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/heart_and_blood_vessel_disorders/biology_of_the_heart_and_blood_vessels/blood_vessels.html
"Blood Vessels." Merck Manual Home Edition. N.p., n.d. http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/heart_and_blood_vessel_disorders/biology_of_the_heart_and_blood_vessels/blood_vessels.html.
"Cardiovascular System." InnerBody. N.p., n.d., http://www.innerbody.com/image/cardov.html.
"The 25 Best Foods For Your Heart." Prevention. N.p., n.d., http://www.prevention.com/health/health-concerns/best-foods-heart-health?s=22.
Lewis, Tanya. "Human Heart: Anatomy, Function & Facts." LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 23 May 2013.http://www.livescience.com/34655-human-heart.html.
*"CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM." INNERBODY, HTTP://WWW.INNERBODY.COM/IMAGE/CARDOV.HTML.
*"NEW RELEASES." 5 WAYS TO PREVENT HEART DISEASE, HTTP://WWW.HEALTH.HARVARD.EDU/HEALTHBEAT/THESE-FIVE-HABITS-CAN-SAVE-YOUR-HEART-HERES-HOW.
*LEWIS, TANYA. "HUMAN HEART: ANATOMY, FUNCTION & FACTS." LIVESCIENCE. TECHMEDIA NETWORK, 23 MAY 2013, HTTP://WWW.LIVESCIENCE.COM/34655-HUMAN-HEART.HTML.
YouTube, 2 July 2022, http://charlottewellnessclinic.blogspot.com/2010/03/different-parts-of-blood.html.