Human body's largest organ is the integumentary system includes
- Skin
- Hair
- Nails
Skin
General Information:
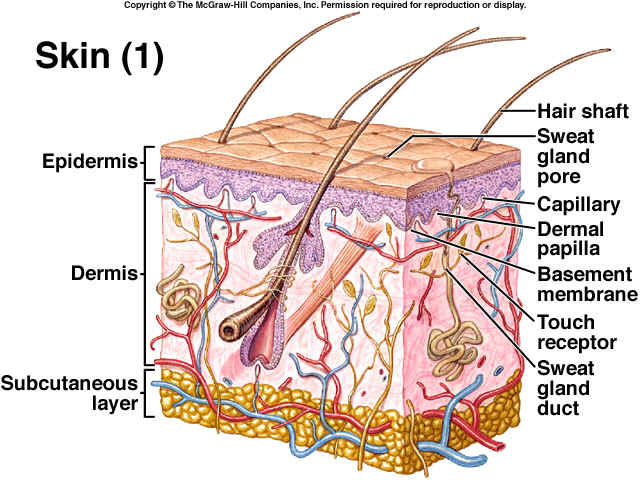
Skin is the largest organ of the human body. It is made mostly of proteins and lipids. On average, skin weighs about six pounds. Skin has three layers: the epidermis, or the outer layer, the dermis, the middle layer, and the hypodermis, the fatty layer.
Skin Proteins:
Collagen: Makes up 75% of skin. Wards off wrinkles.
Elastin: Found in the dermis. Tightens skin.
Keratin: Building blocks of skin.
Skin Care Products
Learn which ingredients are best for skin type and goals.
Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHA)- Targets fine lines and pigmentation, evens skin tone, and reduces age spots and large pores. Sun sensitivity; may cause mild irritation.
Beta-hydroxy acid (salicylic acid)- Treats acne, repairs sun damage, improves texture and tone, exfoliates. Less irritating than AHA.
Hydroquinone- Skin bleacher. Removes dark marks.
Kojic Acid- Lightening agent.
Retinol- Improves pigment, targets fine lines, wrinkles. Improves texture, tone, and color. Skin hydrator.
L-Absorbic Acid- stimulates synthesis of collagen. Targets scars, wrinkles, and fine lines. Contains Vitamin C.
Anti-Agers:
Health Tips:
Sun Damage:
Dangers:
Prevention:
Hair
• Hair, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails
are integumentary accessory structures
– Located in dermis
– Project through skin surface
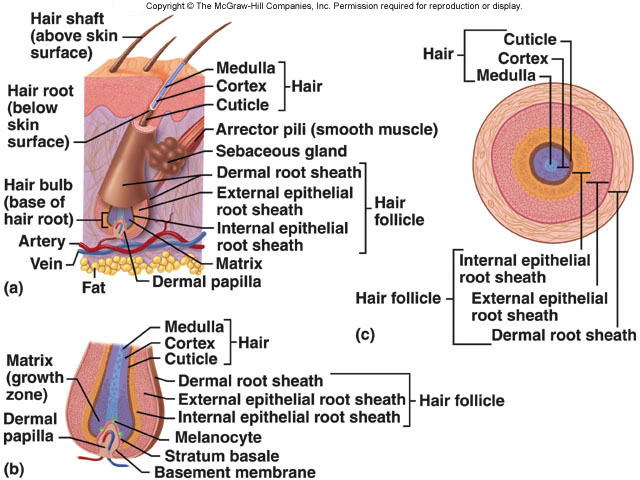
• Hair: nonliving structure produced in organs called hair follicles
– Project above skin surface almost everywhere on human body
• Exceptions include sides and
soles of feet, palms, sides of
fingers and toes, lips, and
portions of external genital organs
• Hair follicles project deep into dermis and often extend into subcutaneous
layer
– Walls of each follicle contain all cell layers found in epidermis
– Base of follicle consists of a peg of connective tissue containing
capillaries and nerves called the hair papilla
• Epithelium at base of follicle forms a cap over this hair papilla
– Hair is formed by repeated division of epithelial stem cells
surrounding the hair papilla
– Hair lengthens as daughter cells are pushed toward the surface
– About halfway to skin surface,
these cell also undergo
keratinization and die
» Marks the boundary between
the hair root (portion that
anchors hair into skin) and
hair shaft (the portion of hair
we see)
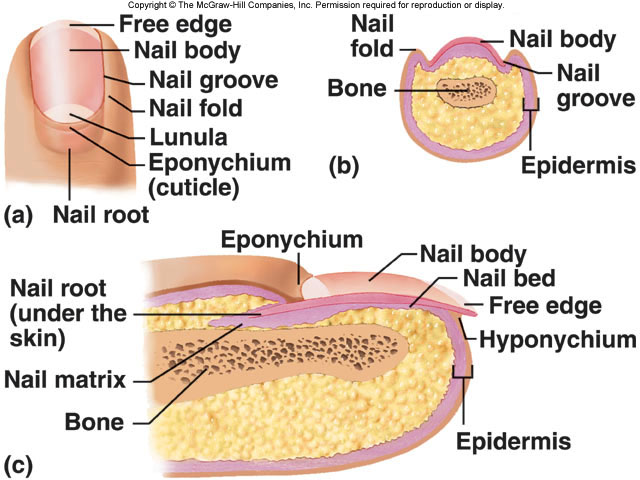
Nails
• Nails: form on dorsal surfaces of fingers and toes
– Protect exposed tips and limit distortion when subjected to
mechanical stress
– Nail body is made of dead cells packed with keratin
• Covers a recessed level of epidermis called the nail bed
• Nail production occurs in a deep epidermal fold not visible from the
surface called the nail root
– Portion of the stratum corneum of this
fold extends over exposed nail near
root, forming the cuticle (eponychium)
– Underlying blood vessels give nails
their pink color
• These vessels may be obscured
near the root, leaving a pale
crescent called a lunula
Sources
http://faculty.southwest.tn.edu/rburkett/integumentary_system.htm
http://www.pennmedicine.org/health_info/body_guide/reftext/html/skin_sys_fin.htm
http://www.rci.rutgers.edu/~uzwiak/AnatPhys/APFallLect7.html
General Information:
Skin is the largest organ of the human body. It is made mostly of proteins and lipids. On average, skin weighs about six pounds. Skin has three layers: the epidermis, or the outer layer, the dermis, the middle layer, and the hypodermis, the fatty layer.
Skin Proteins:
Collagen: Makes up 75% of skin. Wards off wrinkles.
Elastin: Found in the dermis. Tightens skin.
Keratin: Building blocks of skin.
Skin Care Products
Learn which ingredients are best for skin type and goals.
Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHA)- Targets fine lines and pigmentation, evens skin tone, and reduces age spots and large pores. Sun sensitivity; may cause mild irritation.
Beta-hydroxy acid (salicylic acid)- Treats acne, repairs sun damage, improves texture and tone, exfoliates. Less irritating than AHA.
Hydroquinone- Skin bleacher. Removes dark marks.
Kojic Acid- Lightening agent.
Retinol- Improves pigment, targets fine lines, wrinkles. Improves texture, tone, and color. Skin hydrator.
L-Absorbic Acid- stimulates synthesis of collagen. Targets scars, wrinkles, and fine lines. Contains Vitamin C.
Anti-Agers:
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid
- DMAE(
- Hyaluronic Acid
Health Tips:
- Drink lots of water
- Remove all dirt and makeup properly
- Moisturize Eat a balanced diet
- Pay attention to how your skin reacts to certain conditions and environments
Sun Damage:
Dangers:
- skin cancer
- sunburn
- wrinkles
- dry skin
Prevention:
- Use sunscreen with SPF of at least 15 everyday
- Apply sunscreen 20-30 minutes before sun or water exposure. Do not apply wet for most effectiveness
- Reapply every 3 hours ( this varies by person and situation)
Hair
• Hair, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails
are integumentary accessory structures
– Located in dermis
– Project through skin surface
• Hair: nonliving structure produced in organs called hair follicles
– Project above skin surface almost everywhere on human body
• Exceptions include sides and
soles of feet, palms, sides of
fingers and toes, lips, and
portions of external genital organs
• Hair follicles project deep into dermis and often extend into subcutaneous
layer
– Walls of each follicle contain all cell layers found in epidermis
– Base of follicle consists of a peg of connective tissue containing
capillaries and nerves called the hair papilla
• Epithelium at base of follicle forms a cap over this hair papilla
– Hair is formed by repeated division of epithelial stem cells
surrounding the hair papilla
– Hair lengthens as daughter cells are pushed toward the surface
– About halfway to skin surface,
these cell also undergo
keratinization and die
» Marks the boundary between
the hair root (portion that
anchors hair into skin) and
hair shaft (the portion of hair
we see)
Nails
• Nails: form on dorsal surfaces of fingers and toes
– Protect exposed tips and limit distortion when subjected to
mechanical stress
– Nail body is made of dead cells packed with keratin
• Covers a recessed level of epidermis called the nail bed
• Nail production occurs in a deep epidermal fold not visible from the
surface called the nail root
– Portion of the stratum corneum of this
fold extends over exposed nail near
root, forming the cuticle (eponychium)
– Underlying blood vessels give nails
their pink color
• These vessels may be obscured
near the root, leaving a pale
crescent called a lunula
Sources
http://faculty.southwest.tn.edu/rburkett/integumentary_system.htm
http://www.pennmedicine.org/health_info/body_guide/reftext/html/skin_sys_fin.htm
http://www.rci.rutgers.edu/~uzwiak/AnatPhys/APFallLect7.html