Cervical Cancer
General Infomation
- Cancer is a disease in which certain body cells do not function correctly, divide very fast, and produce to much tissue that forms a tumor.
- Type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix.
- The lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina.
- The virus survives for years.
- Controlled to the process that causes some cells on the surface of the cervix to become cancer cells.
- cervical cancer caused by a virus called HPV
Types of Cervical Cancer
- Squamous cells caranomas
- Adenocoarcinomas
- Many sexual partners
- Early sexual activity
- Other sexually transmitted infections
- A weak immune system
- Cigarette smoking
What is HPV?
- HPV is short for human papilloma virus
- This virus can cause changes in the cervix
- HPV is NOT the same as HIV
- HPV is not a new virus but we are learning more about it
- Most men and women who have ever had sex have had HPV at some time in their lives
Signs
- Women with early cervical cancer and pre-cancer usually have no symptom
- Signs cal also cause by conditions other than cervical cancer
- Ignoring symptoms may allow the cancer to progress to a more advanced stage and lower your chance for effective treatment
http://cervicalcancer2010.weebly.com/uploads/4/1/4/8/4148636/9273858.jpg?483
Symptoms
- In the early stages of cervical cancer women do not usually experience any symptoms
- Cervical cancer diagnosis comes as a surprise because of the absence of noticeable symptoms
- Irregular vaginal bleeding, abnormal vaginal discharge,bleeding during intercourse
- Pelvic, back or leg pain, weight loss, bleeding with urination or bowel movement
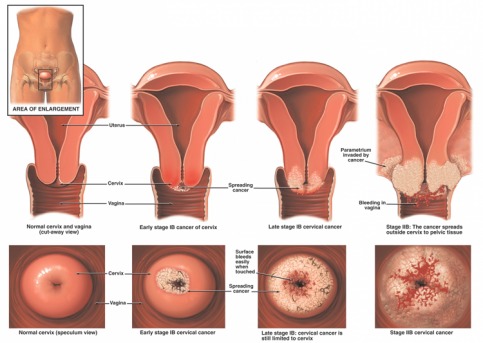
Stages/Staging
- Info from exams and diagnostic tests is used to determine the size of the tumor.
- How deeply the tumor has invaded tissues in and around the cervix and the spread to lymph or distant organs (metastasis)
- A cancer that comes back or spreads is still referred to by the stage it was given when it was found.
- Imaging tests
- Visual examination of your bladder and rectum
www.macmillan.org.uxk/Cancerinformation/Cancertypes/Cervix/Treatingcervicalcancer/Radiotherapy/Radiotherapy.aspx
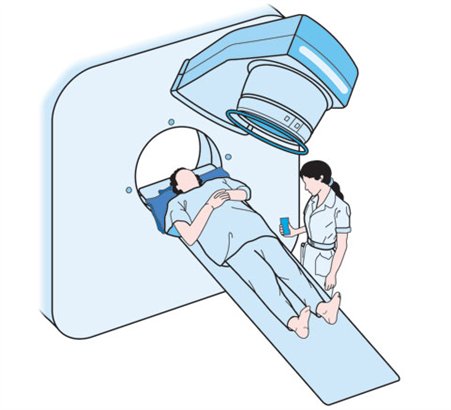
How to treat Cervical Cancer? / Treatments
- General treatment info
- After establishing the stage of your cervical cancer
- Depending on the type and stage of your cancer, you may needed more than one type of treatment
- Earliest stages of cervical cancer either surgery or radiation combined with chemo may be used.
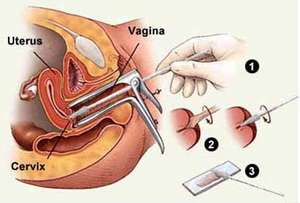
- A detailed vaginal and rectal exam is typically the initial intervention to determine the stage of the disease (where the cancer may have spread)
- Treated with radiation that may be include a small dose of chemotherapy to "sensitive" the cancer cells to radiation
http://www.cervicalcancerdoc.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/picture-illustrating-a-cervical-cancer-treatment.jpg?6521bd
What you can do?
- Write questions to the doctor
- Make a list of your medication
- Note any personal history that increased your risk of sexually transmitted infection, such as early sexual activity, multiple partners or unprotected sex
- List medication
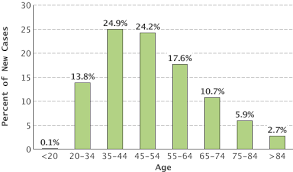
Who can get Cervical Cancer?
- Some women have a greater chance of getting cervical cancer if they:
- Have HPV and it doesn't go away
- Have HIV or AIDS
- Smoking
http://rochester.edu/news/show.php?id=5382
8 Trending in: Cervical Cancer/ HPV Vaccine
- Oral HPV can be transmitted by oral -to-oral, oral-to-genital routes
- HPV vaccination not linked with risky sexual behavior among teenage girls
- New transport system for DNA vaccines could help treat HIV, malaria, HPV, and other major illnesses
- Women with mental illness are 40% less likely to receive routine cancer screenings
- Memory complaints link to stroke risk for the highly educated
- More than salt, sugars may contribute to high blood pressure
- Brain study shows inflammation is a maker of autism
- Zinc test for early breast cancer looks promising
Survival Rates
- Some patients with cancer may want to know the survival statistics for people in similar situations, while others ma not find the numbers helpful
- People survive at least 5 years
- Survival rates are often based on previous outcome of large numbers of people who had the disease
http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/cervix.html